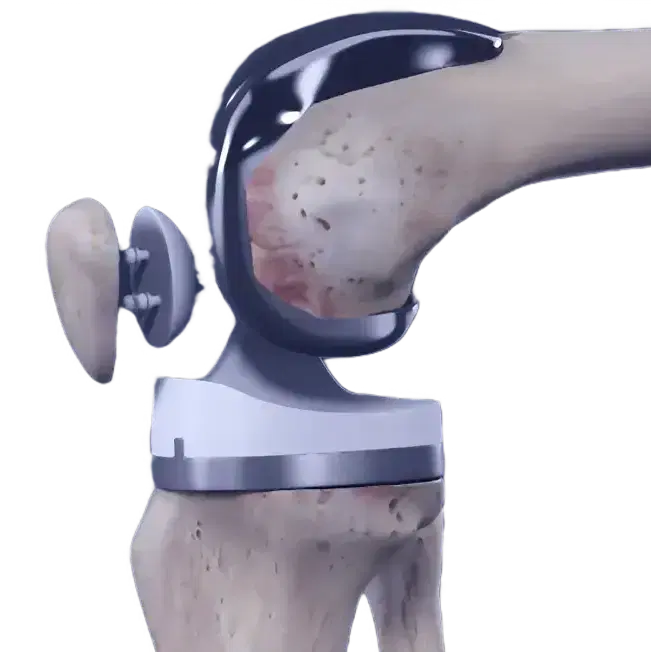
What isthe meniscus?
The meniscus acts as a knee "shock absorber" between the thigh (femur) and leg (tibia) bones. It reduces load transmission, provides stability, and helps disperse fluid around the knee joint.
There are two menisci in each knee. One on the inner side (medial) and one on the outer side (lateral) of the knee

Is the meniscusthe same as cartilage?
The knee contains various types of cartilage. Hyaline cartilage lines the ends of the bones, providing a smooth surface. The meniscus, a fibrocartilage, differs in properties and composition.
To avoid confusion, I refer to the bone lining as "cartilage" and the meniscus as the "shock absorber."

How is the meniscus injured?
The meniscus is commonly torn during a twisting knee injury, when it gets trapped forcefully between the thigh (femur) and leg (tibia) bones. This can happen alongside other knee injuries, like anterior cruciate ligament rupture. Often, patients cannot recall the exact incident that caused the meniscus tear.
What are the
meniscal tear symptoms?

Swelling
The swelling, when present, usually fluctuates with activity and settles with rest and medication

Pain
Meniscus tears commonly cause sharp, sudden stabbing pain, especially during deep bending or twisting movements

Locking episodes
The loose piece of meniscal tissue gets intermittently caught between the two bones of the knee
How is the diagnosis made?
The meniscus acts as a knee "shock absorber" between the thigh (femur) and leg (tibia) bones. It reduces load transmission, provides stability, and helps disperse fluid around the knee joint.

Incomplete tear

Radial tear

Horizontal tear
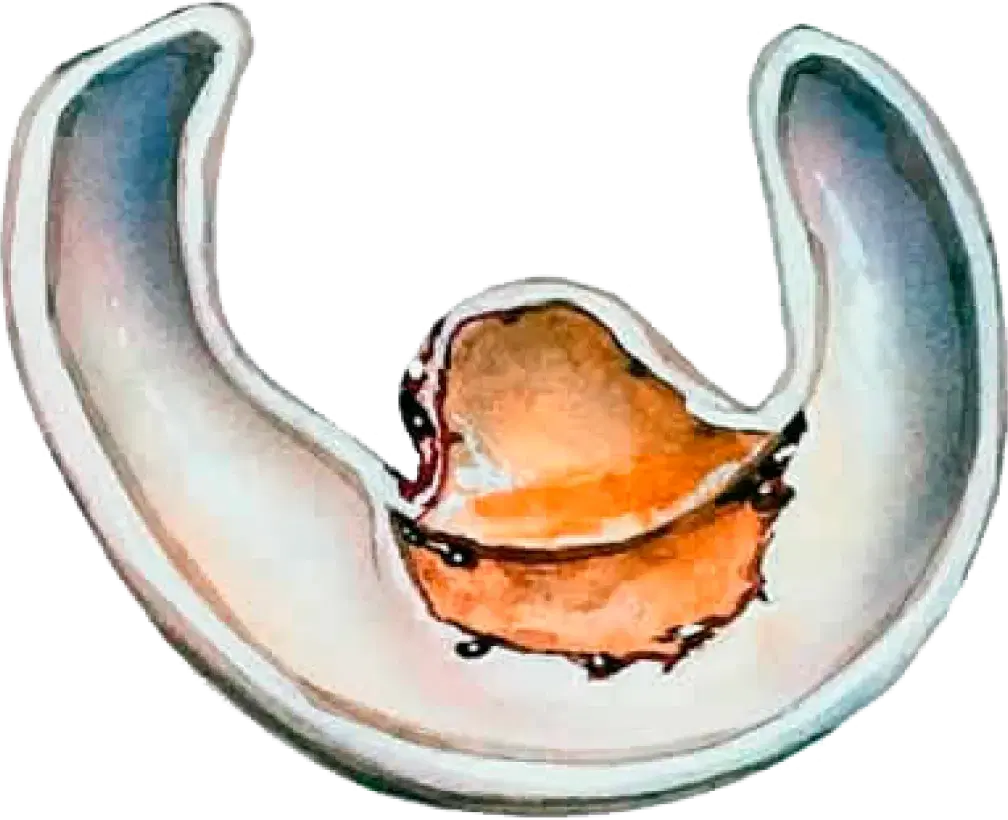
Flap tear

Complex tear

Bucket-handle tear
When should you operate on a meniscus tear?
Most meniscal tears initially receive non-surgical treatment for 3-4 weeks.
If symptoms are improving, there is no rush for surgery. However, if symptoms persist beyond 6-8 weeks without improvement, surgery may be considered.
What are the treatment options?
Initial treatment for meniscal tears typically involves RICE (rest, ice, compression, elevation) and the use of over-the-counter pain relievers like non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
What are the indications to perform early surgery?
In rare cases, a locked knee may occur when a meniscus tear causes limited or no movement. Semi-urgent surgery is advised to unlock the knee and prevent further damage.
Similarly uncommon, a large meniscal tear called a bucket handle tear may not affect motion but can damage the knee's normal cartilage if left untreated.
Is the meniscus
removed or repaired?
In the majority of cases the meniscus tear is unable to be repaired and is removed
Meniscus tear (up) and post meniscectomy (down)


What determines if a meniscus can be repaired?
Many factors are considered, includingHow is the
meniscus removed?

The meniscus is surgically removed using keyhole arthroscopy.
Two small incisions are made in the knee: one for a camera and the other for instruments like scissors and shavers. Fluid is used to inflate the knee for better visualization during the procedure.
How is the
meniscus repaired?

Meniscus repair is done through keyhole arthroscopy, typically with two stab incisions in the knee.
The tear is assessed for repairability, and sutures or suture darts are used for the repair. Additional incisions may be necessary for completing the repair process.

What happensif I lose my meniscus?
Loss of a portion of the meniscus can lead to increased stress on the articular cartilage that lines the knee.
We know that if the entire meniscus (100%) is removed, that side of the knee, which now has no meniscus, will develop arthritis in 20-30 years time. Thankfully, in the vast majority of cases much less than 100% of the meniscus is usually removed (most commonly 30%). The general principle is to remove as little of the meniscus as possible to improve the patient’s symptoms.
If the adjacent cartilage is already worn (pre existing osteoarthritis), then the likelihood of progression of the arthritis is higher.
Will it heal by itself?
Certain meniscal tears can heal, especially smaller tears located in the periphery of the meniscus where there is better blood supply. The healing potential is further increased if the tear is accompanied by an ACL rupture. However, the ability of the meniscus to heal diminishes with age.
Can you have a meniscal tearand have no symptoms?

The incidence of a meniscal tear with no symptoms, diagnosed incidentally on a MRI scan is approximately 5%.
This percentage increases with increasing age.
For example, if you have pain on the inner side of your knee (medial side) and the MRI shows a tear in the meniscus on the outer side (lateral) then it is likely that your meniscal tear is asymptomatic and the cause of your pain is something other than the meniscal tear.

Do you need a
Knee replacement?
Dr Seeto in affiliation with Medibank Private and East Sydney Private hospital, offers a program for eligible Medibank Private Members, to eliminate medical out of pocket costs for your Knee Replacement.
The program includes a pre-surgery preparation program, spending the minimal time necessary in hospital, as well as home rehabilitation if necessary.
Book a consultation
today
9:00 am - 4:30 pm